As a Magento B2B e-commerce development company, we know everything about financial transactions in online stores. Our experts are good even at integrating blockchain into the payment process. Check it yourself!
Blockchain in eCommerce overview
In order to attract and retain clients, 85% of businesses with more than $1 billion in annual sales are using blockchain-based payment methods (you. The blockchain is a decentralized, public ledger that records all transactions.
Many advantages, such as lower costs and risks, faster speeds, more secure data storage, and access to previously emerging markets and demographics, are made available to online retailers by this innovation.
We’ll take a look at the fundamentals of blockchain technology first, then move on to actual implementation. So, blockchain in eCommerce and other sectors:
- what is it?
- why is it important?
- when could you use it?
In this post, we’ll also examine the technical aspects of this innovation and give a better idea of how smart contracts are made, used, and analyzed. Finally, we’ll look at the potential uses of blockchain technology for online stores. Keep reading!
How Blockchain solves trust issues
Essentially, a blockchain is a decentralized database that keeps track of transactions via an ever-expanding chain of chronologically ordered data blocks. Cryptographic connections are used to join these blocks together. Each block also includes a date, hash code of the prior block, and transaction information.
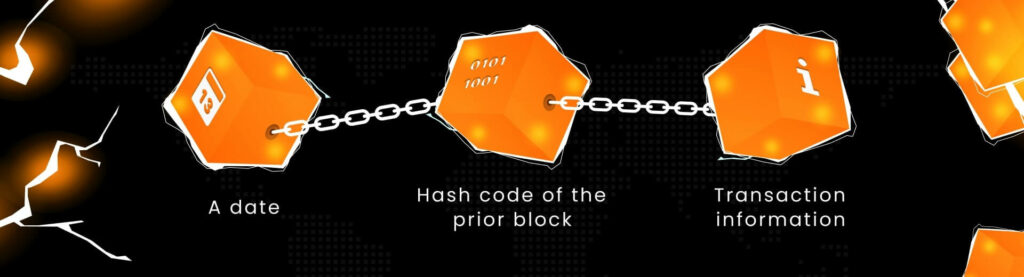
A blockchain in eCommerce is used to record transactions across multiple computers in a way that prevents any single computer or node from manipulating the ledger. So it’s impossible to compromise the integrity of the entire chain.
Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies were the first to make use of blockchain. Together with several distinct payment methods being in trend now, they are commonly employed by online stores. The goal was to build a user-owned, decentralized financial system independent of regulators, banks, and governments. As a result, individuals could take charge of their financial lives and communicate directly with one another, cutting out the need for middlemen.
Moreover, blockchain developers recognized the issue that you cannot quickly access your funds if they are stored in a bank account. Each transaction you make is really a command to the bank to carry out a certain operation on your account. In this case, various risks arise, such as a bank default or various restrictions on operations.

And this brings up a few more issues. You must first feel confident in the bank’s stability and trustworthiness. As a second point, you have to hope that the bank will let you utilize your account. The third is that your cash isn’t sitting in your hands but rather in the hands of those responsible for its safekeeping and administration.
So blockchain technology addresses these issues thanks to its characteristics:
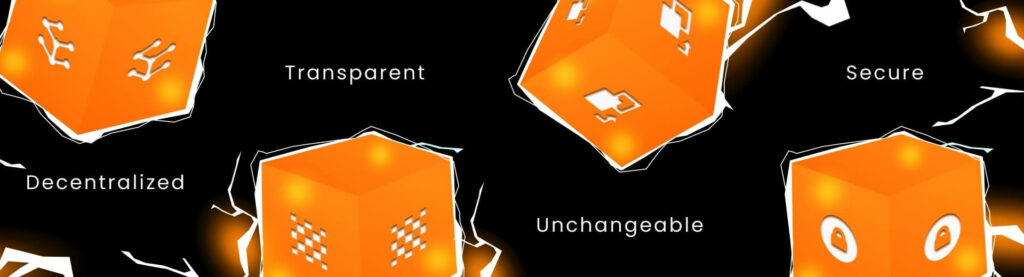
- Decentralized: there is no central authority making or vetoing decisions, and all transactions are processed and validated by blockchain nodes in real time. Even if any component of the network was to go down, the data would still be accessible and transactions would be completed by the remaining nodes.
- Transparent: blockchain is open and accessible, allowing users to view the transaction history and balance of any given address. However, this does not exclude anonymity. For instance, identifying the wallet’s true owner might be challenging if you aren’t already acquainted with them.
- Unchangeable: The blockchain’s algorithms allow for the addition of data to the ledger, but prevent any manipulation of the existing records. Once a transaction has been recorded in the system, it can no longer be undone. By doing so, the data within the blockchain is assured to be accurate and the possibility of fraud is much diminished.
- Secure: Due to its decentralized nature, wherein a lot of nodes contribute to the process, it is extremely difficult to hack. To clarify, this may be done with a local node on your computer, but when you attempt to update the blockchain, other nodes will detect the discrepancy and reject your modifications.
By the way, announcing that you adopt Blockchain in your store can be one of the ways to upsell your products. Learn more about some other strategies here.
Innovative ways of adopting Blockchain
We have discussed blockchain in eCommerce in terms of finance, but since its inception, the use of this technology has come a long way. And here we’ll give some fresh examples.
There is an organization called Hyperledger, which creates commercial industrial blockchains, and it is not associated with cryptocurrencies. So Hyperledger, Walmart, and IBM together created a product quality control system.
One of the problems that Walmart had was tracking contaminated products and products from the places where various epidemics originated.

For example, if a product arrived at their store, the buyer bought it and became infected with E. coli. First, Walmart must pull all potentially affected products from shelves, then it must identify which goods are contaminated and remove only those from shelves.
For the sake of argument, let’s take mango. Possibly from Asia, Africa, or South America; E. coli, on the other hand, was only ever found in Africa. And you must identify the rare African mangoes and collect them.
In some cases, tracking out the origin of the products took as long as seven days. This time was decreased to 2.2 seconds after deploying the blockchain, which they utilized as a tracking system to trace the route from the farm to the customer. You can read more about this case study here.
“A new, Blockchain-enabled Walmart Food Traceability Initiative was created to increase transparency in the food system and create shared value for the entire leafy green farm to table continuum.”
Walmart
To round off our analysis of this system, let’s think about it from the perspective of trust.
For instance, if your firm is the sole link in the supply chain, you will be responsible for any losses incurred at any point in the chain. There is no point in deciding whether to trust someone or not under these circumstances.
However, if each step is handled by a different entity, a certain level of mutual confidence is required. Another option is to create a blockchain and distribute it to all of the operators. The information people input won’t be altered.
This way, we can see which institutions are slacking off in their duties. It allows us to keep tabs on:
- when the products were delivered
- how much they weighed at each step
- what condition they were in when they were shipped.
That is, applications for the blockchain extend far beyond the financial sector.
How Blockchain transactions work
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s get into the technical details. First, let’s take a look at the functioning of the blockchain and the flow of the transaction.
Blockchain is a chain of blocks that are made up of transactions and can’t be changed after they are created.

- After an agreement is reached and signed, the transaction can officially begin. In other words, now that you know the address of the intended receiver, you may sign to confirm the transaction and transfer the desired amount to the designated location.
- To achieve this, you’ll need a client that can connect with the node; this is accomplished with the use of a software wallet, which may be installed on your computer, mobile device, or web browser.
- The next step will be an attempt to add this transaction to an existing block. The block is sent to all validating nodes for verification.
- Each node receives a reward for the work it does during block generation and verification, which includes doing computations and attempting to generate a valid block. The reward may include both an internal network incentive and a user-initiated transaction fee.
- Each new block added to the chain triggers a full network refresh, during which all nodes exchange information and ensure that all the data is up to date. Once the network has been updated, the transaction is considered finalized.
Blockchain wallet
Let’s make a brief review of a software wallet and a blockchain wallet. Those two things are intentionally defined apart.
A blockchain wallet is simply your address on the blockchain network. When you create it, you get 2 keys – public and private. The public key is the address on the blockchain, and the private key is the password.

You may think of your public key as your email address, which means anybody can know it and send you transactions using it. A private key, meanwhile, serves as your account’s password.
A software wallet‘s function is to safely store your private key and enable you access to the blockchain wallet.
Let’s take an example of an email. The email server where information about your letters is stored is the blockchain itself, your node. And the web interface with which you view these letters is a software wallet.
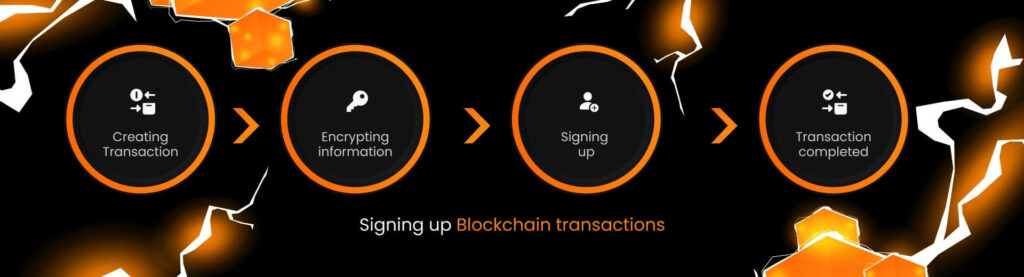
Signing up Blockchain transactions
How is a transaction signed? This is a general scheme, which is not particularly needed for use, it might be useful for understanding.
When a transaction is created and signed, it is encrypted. Let’s consider it in more detail.
- When one wants to make a transaction, the associated information is always encrypted using the recipient’s public key.
- Then one uses their private key to confirm that they want to send this encrypted message, which means signing it up. Only after this step, the transaction is made.
- A recipient, in turn, uses their private key to decrypt the information. This way they can see a transaction’s content and a sender’s address, thereby determining who sent the money.
Let’s assume we have a transaction and all of its associated data (the data itself may or may not be encrypted – it depends on the blockchain). We put our private key on it, indicate the public key of the receiver, and send it to the network. The rest is made by the blockchain mechanism.
And once everything has been double-checked, the transaction is added to the block.
Block creation and functioning
Let’s have a little discussion regarding blocks:
- how they function
- the process through which a block is made.
Multiple transactions’ hashes are recorded in the blockchain. What this means is that their content is conveyed in a single line that is always presented at the same length. The term for this process is “hashing.”
Then, each of these hashes is combined with the previous one to create a new hash, and so on, until a single hash of all transactions is generated and added to the block.
The block also includes:
- the timestamp
- the preceding block’s hash.
Blockchain in eCommerce: user interaction mechanism
Now that we’ve covered the blockchain’s technical underpinnings, we can go on to discuss how it may be put to use.
First and foremost, understand that the blockchain is a secure, closed system.
To put it another way, there is no IP address in the blockchain to which one might send a request and receive a response. It is necessary to set up a local node on your computer in order to interact directly with the blockchain. It will then be available on the local host through the specified port.

Second, in order to communicate online, so-called public nodes are used.
In addition to the blockchain’s native API, public nodes typically offer a web interface with an API of their own. A request sent to the public node will be sent to its local node, which will then process and respond to the request. This may be viewed in the software wallet’s user interface or the source code.
The operation of a typical software wallet looks like this.
- They employ public nodes hosted by other parties and route wallet-originated requests to the relevant nodes. Here, the wallet and other decentralized web3 apps are the primary means of user interaction. Wallet integration is possible if you allow these applications access. But what is meant here is public keys, not private ones.
- As soon as the program detects your public key, it knows you want to take some action. You’ll be prompted to sign your transaction using a private key if the wallet verifies that you intended to do this operation.
- When you confirm an action by signing it, the app will submit the transaction to the decentralized system.
Sending methods are flexible, of course. But to either the public node or your local node server, it will be sent via your wallet after being signed.
Now that we’ve covered the fundamentals of how the blockchain in eCommerce works, we can move on to smart contracts. Keep reading about it in the second part of the article. And If you want to learn more about any kind of eCommerce development services, check our Magento development services page.
