The adoption and integration of CI/CD methodology in the application development process is a powerful tool that allows achieving high quality of each code commit and the final product as a whole. It also reduces the overall development time, increases communication between different teams involved in the project, and much more.
The latest “Puppet state of DevOps” report demonstrates its effectiveness in several ways, including a 5-fold decrease in failure rate, 440-fold acceleration in the commit-deployment phase, and a 46-fold increase in deployment rate. The report also found that when developing applications using CI/CD, teams could spend 44% more time writing code for new features instead of digging into processes and customizing tools. This article outlines the main features of the CI/CD pipeline and its benefits for business. After reading it, you will understand why more and more companies worldwide use this release CI/CD automation approach.
Business Benefits of CI/CD
Before we move on to the benefits of this methodology, let’s answer the question, “What is CI/CD for eCommerce?” to ensure we are on the same page.
CI/CD stands for Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery, which represents a methodology for the software development lifecycle. This set of principles and practices aims to automate the testing and delivery of new modules of the developed project to all stakeholders (developers, analysts, quality engineers, and even end-users). The CI/CD workflow is based on the principle of regularly deploying small code portions that make minor changes to the overall structure, which is much more efficient and profitable for the entire project, rather than assembling all the changes into a massive batch, deploying at one time.
Let’s take a look at the advantages of the CD pipeline compared to the traditional method.
СI/CD Workflow’s Benefits

1. Decrease of failure and its impact to project
As already mentioned, CI/CD is based on integrating small batches of code but with high frequency. In doing so, each code is tested as soon as it enters the repository. This approach enables the immediate detection and correction of errors and bugs, preventing a snowball effect. As a result, it reduces the risk of encountering a critical error that could disrupt the entire application and necessitate rewriting a whole section of code from scratch. It, in turn, causes delays in project delivery and financial and reputational losses. As remote work becomes common and teams are spread across the globe, using a CI/CD workflow is increasingly important and needed in today’s developer environment.
2. Release rate accelerating
The next advantage naturally stems from the previous one: the faster errors and bugs are fixed, the sooner the project can move to the release stage. Continuously writing new code is essential to the CI/CD pipelines. This means the development team incrementally integrates new code, gradually building up the system in preparation for its release. This approach enables businesses to be more adaptable to changing market conditions. For example, suppose there’s an urgent need to integrate a new feature to remain competitive. In that case, the team can shift their focus seamlessly, ensuring that the previous development work remains valuable rather than becoming a burden.
3. Productivity advancement
With an efficient process for identifying and troubleshooting bugs and errors, product specialists can focus more on writing and deploying new code, resulting in higher-quality products. They no longer need to search for solutions to critical bugs that emerged months ago and disrupted functionality. This is where the CI/CD workflow comes into play, allowing developers to integrate new code into the main branch continuously. This code is of high quality and thoroughly tested by the QA team. Any bugs are addressed at their source, preventing them from spreading throughout the entire application.
CI/CD Process: Step by Step
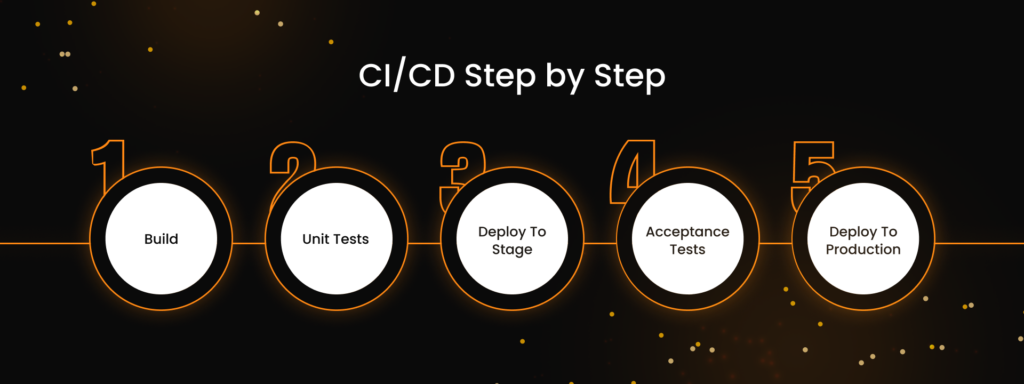
Continuous integration (CI)
The CI is the primary, basic software creation process. All code-level changes are brought into a single central repository and merged into the main branch. After each merge (which takes place several times a day) in the modified system, there is an automatic build (often the application is packaged in Docker) and testing (checking of specific code modules, UI, performance, and API reliability). In this way, developers are insured against too late detection of problems.
Continuous delivery (CD)
The CD is the next level after CI. A new version is created and tested with every code change registered in the repository. Also, developers can quickly launch it with a single click of the deploy button. However, the deployment is still run manually. This method allows you to release changes in small batches, which can easily be changed or eliminated when needed.
Continuous deployment (CD)
Once the release is automated, one manual step remains: approving and running the deployment in production. Continuous deployment eliminates that, too, without requiring direct approval from the developer. All changes are deployed automatically.
Using continuous deployment, your team will stop seeing release day as the beginning of the apocalypse. In addition, developers immediately see their work’s results in action, which motivates them to do their tasks better and faster. Continuous deployment also offers some additional benefits::
- Given the fast pace of the development process, since every change is transmitted automatically, a release has a negative impact on the process. However, it does not prevent developers from creating code.
- Because changes are made in small batches, fixing them does not entail a significant crew effort.
- The cherry on the cake is that continuous deployment increases the user experience of the product. Users can see the improvements being made literally in front of their eyes.
Release pipelines
In essence, a release pipeline transfers written code to production. A traditional release pipeline consists of several steps that follow one after the other. In exceptional cases, highly complex pipelines, some of the stages may be carried out in parallel. So, what components are included here:

1. Repair and restart
The main task is to fix problems that have occurred and to restart tasks that have failed. Moreover, this is an optional phase, and not all conveyors support repair and restart, so use this reasonably.
2. Tasks
Tasks are lists of activities and tasks that need to be completed for a successful release. Note that tasks can be performed in any order. The main thing is to complete them. Look at stages as a tool for flow management and tasks as processes to be completed.
The following tasks are for completion:
Providing infrastructure
This includes various tasks, from creating new virtual environments for testing to setting up and optimally configuring the test environment. In addition, this can also have the integration and launching of additional services, such as a web server.
Deploying applications
Additional changes in the environment’s configuration can be made if necessary at this stage. Packaged software is then deployed on this infrastructure.
Testing
Testing and fixing the results. It is essential to note which stages were successful and which failed during testing activities.
Shutting down the infrastructure
Once the testing phase is completed, any virtual infrastructure can be shut down or even wholly decommissioned to save money.
3. Artifact store
To ensure fast and problem-free software deployment at every stage, from code modifications to the deployed application, developers must have continuous access to all digital artifacts of the project. Such a repository is the artifact store.
In addition, the artifact repository must be configured to support different versions of the artifacts. The artifact set for a single build and release must be atomic and separate from the artifacts of other releases to prevent cross-contamination.
4. Configuration store
The configuration repository contains values that are the same for all the assemblies (connection strings, API URLs, etc.) in contrast to the artifact repository, which includes different data specific to each build and release individually.
An essential aspect of the configuration repository and the CI/CD pipeline, in general, is security and encryption because inside it, the production configurations are stored, no matter that they can be just machine names.
5. Logging
Sooner or later, malfunctions occur in a pipeline that requires the intervention of experts. To identify the root of the problem, engineers need to examine the logs to understand the issues and what went wrong. The more organized the system and structure of logs is, the less time it will take to isolate problems.
Each element of the log should have the minimum necessary description:
- Release Conveyor/Application
- Conveyor stage
- Assembly number
- Timestamp
6. Metadata store
The metadata repository is one of the most straightforward features of the whole CI/CD approach. This repository contains name/value sets specific to the assembly data. Typically environment variables, but the metadata repository can also collect information about completed tasks and pipeline stages.
7. Execution engine
The release conveyor also includes a component responsible directly for executing the conveyor itself. There are many workflow mechanisms, and how this works under the hood is up to the solution. One standard option that you can use is the bash script.
8. Process viewer
Another option is the graphical representation of your CI/CD pipeline. That way, you can see what processes are going on in the entire workflow. In terms of code, this is the smallest part, but in terms of functionality and manageability, the UI importance is hard to overestimate
How to automate releases
Every year, the CI/CD for eCommerce workflow develops and becomes more and more popular and in demand. The number of benefits it brings is constantly increasing. More and more developers leverage automation release options and consistent integration and deployment workflow – the product is always ready for release, the twin reactions to errors in the code thanks to atomized testing, the list goes on.
To harness the automated release process, you should follow these steps:
- Build tests for the critical codebase element.
- Use CI software to automatically run the tests as soon as batches of code are integrated into the main branch.
- Remember that your engineers should contribute their changes recurrently (daily preferable).
- Resolve any issues with the build as soon as they are detected.
- Each new story requires new test measures.
- Utilize automated rolling deployment tools to activate the code in the new environment. Continuous deployment pipelines allow for undoing failed deployments.
- Use CD pipelines for monitoring and notifying to obtain full-sided control over the process.
Summary
CI/CD for business is the solution you should look at short to get the most out of your work. Let your developers solve exciting problems and conquer the heights instead of routinely writing code, finding bugs, and fixing them.
IT Delight experts are always ready to consult you on establishing an automation strategy and providing full CI/CD implementation support. Contact us to automate your company’s releases or for any eCommerce implementation services.
